Setup a Low-budget NAT Instance
Network Address Translation (NAT)
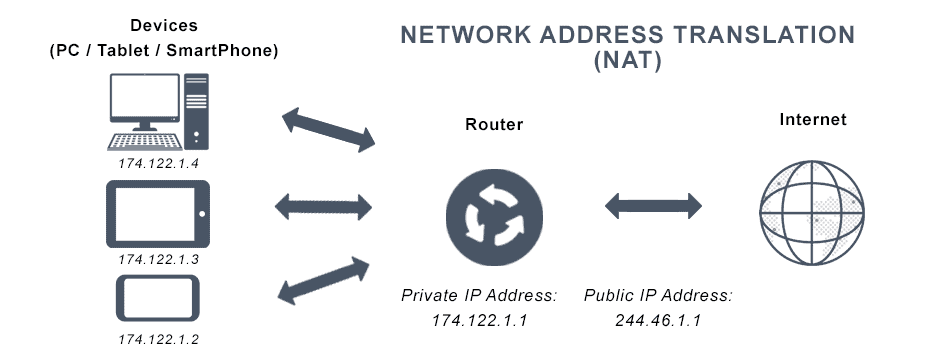 Image: avinetworks (opens in a new tab)
Image: avinetworks (opens in a new tab)
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a method that allows multiple devices on a local network to share a single public IP (IPv4) address to access the internet. The reason for using NAT is to reduce the number of public IP addresses required for a network. As you know that the number of IPv4 addresses is limited (~4.3 billion), and the demand for public IP addresses is increasing rapidly. Additionally, NAT provides a layer of security by hiding the internal IP addresses from the external network.
Initially, NAT was used to extend the life of IPv4 addresses until IPv6 was widely adopted. However, IPv4 addresses have been used for more than 30 years, and the transition to IPv6 is still slow. Consequently, NAT is still widely used in many networks, including home networks, small businesses, and cloud environments.
On AWS, the recommended method for setting up NAT is to use a NAT Gateway (opens in a new tab), as it is a managed service that scales automatically and requires no maintenance. However, the NAT Gateway is not cheap, if not expensive for small workloads such as personal projects or development environments. At the time of writing, the NAT Gateway costs $0.045 per hour plus $0.045 per GB data processed in the cheapest region (N. Virginia). It means that if you run a NAT Gateway and not use it, you will still be charged at least $32.4 per month.
Therefore, setting up an NAT instance is one of the cost-effective alternatives to the NAT Gateway in development and testing environments.
Lab Overview
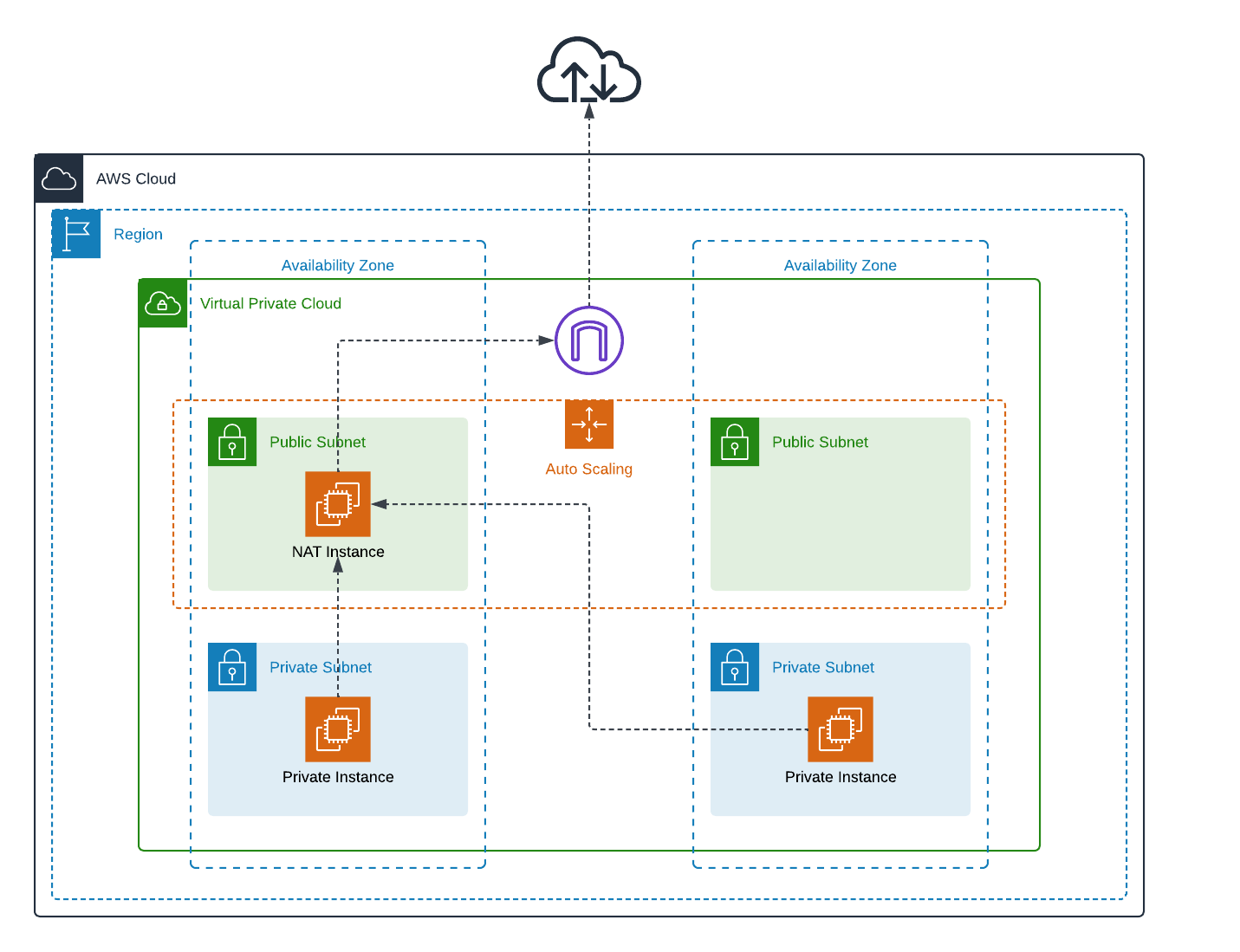
In this lab, we will set up NAT with an EC2 instance (also known as NAT instance). The NAT instance will allow the instances in the private subnets to access the internet through it. An Elastic Network Interface (ENI) will be created and attached as the secondary network interface to the NAT instance, it is responsible for receiving the traffic which comes from the private instances and forwarding it to the internet. We will also put the NAT instance in an Auto-Scaling Group to ensure that the NAT instance would be automatically recovered if it is terminated (intentionally or unintentionally).
The cost of running a NAT instance in this setup is low. If you run the t3.micro On-Demand instance in the us-east-1 region, the cost will be around ~$7.5 if you run it for a month. It could be less if you use newer instance type generations like t4g.micro. The ENI is free, and you are not using any other AWS services that incur additional costs except for the data transfer out of the NAT instance to the internet. More details can be found here (opens in a new tab).
Prerequisites
Before you begin this lab, you need the following:
- An AWS account with the necessary permissions to create and manage resources. If you don't have an AWS account, you can create one here (opens in a new tab).
- Basic knowledge of AWS relavant services like EC2 and VPC.
- How to use basic terminal commands.